Cloud Computing vs Edge Computing: Partners or Deadly Rivals?
Cloud computing vs edge computing, the discussion seems to be unending on their respective pros and cons. Cloud computing is the earliest known network structure enabling data storage over the internet. The added advantage is the ease with which it allows access to that particular data from any device just by having a strong internet connection and desired permissions.
Companies whether on large scale or of small nature are continuously shifting their applications to the cloud. The growth is significant. A large portion of a company’s budget is believed to be dedicated alone to cloud computing. A strong belief suggests that cloud computing itself is the one that enabled the concept of Edge computing.
Having a similar approach to cloud computing, but brings the data nearer to the end-user is the central concept behind Edge computing. Edge computing is believed to have a strong future. Experts strongly believe in the dominancy of Edge computing. A large portion believes that it will shorten the run of cloud computing at the top. With its numerous advantages and popularity. Edge computing is surely shaping up the future of an organization’s data storage and relevant digital transformations.
Cloud Computing- Pioneer of Remote Services:
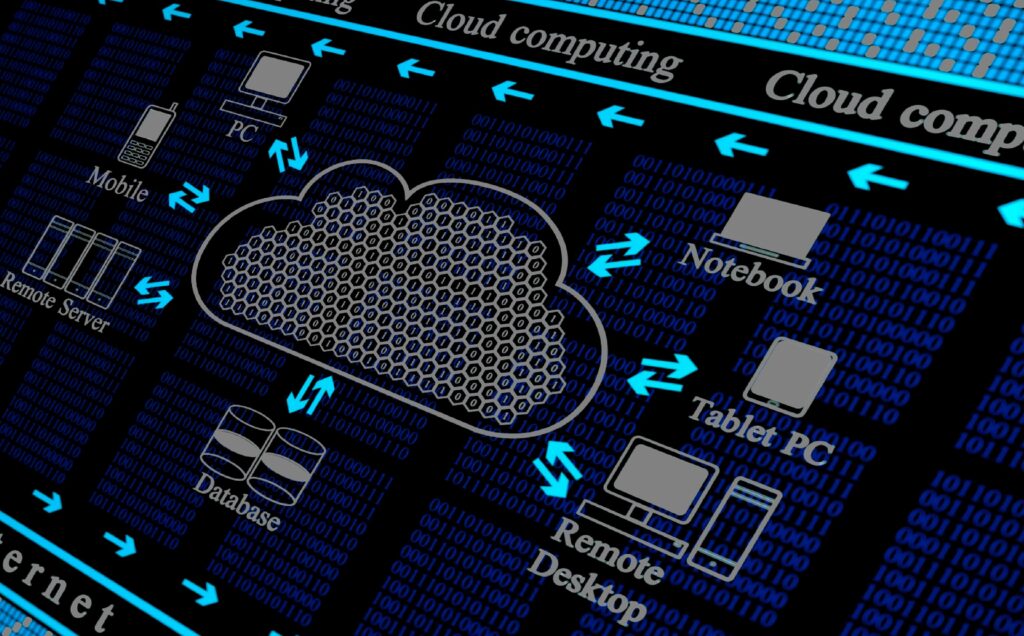
Cloud computing can be simply described as, the on-demand delivery of IT services and resources over the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. These IT services/resources include storage databases, servers, networking, and analytics over the internet. In cloud computing, all the data is collected and managed in a centralized location. Often in a data centre. This approach ensures security protocols to be managed properly. At the same time, allowing reliable remote access.
In simple words, assets and information are stored in a cloud, allowing authorized users to have the access to information from any location at any time. We as individuals are unintentionally surrounded by cloud computing. The domain of cloud computing is far beyond accessing files on multiple devices. Cloud computing allows users to store information from anywhere such as in Google Drive & Dropbox.
One can backup picture, videos, etc using cloud computing. Organizations of every tier and type are adapting to cloud computing. Moving ahead of conventional Business IT resources. Obvious reasons and benefits are compelling companies to look towards cloud computing. First and foremost, cloud computing banishes the needs of purchasing hardware & software, their maintenance and power management, IT experts for handling the infrastructures. Saving huge expenses. Increasing productivity and most importantly saving time.
Big cloud computing services run on a huge network across the world within secure data centres, which are continuously upgraded. Ultimately increasing the performance. Cloud providers offer a prescribed set of policies ensuring overall security. Protecting assets and information from potential security threats.
Cloud Computing Models:
There are various models of clouds. Each of them varies as per the desired requirements.
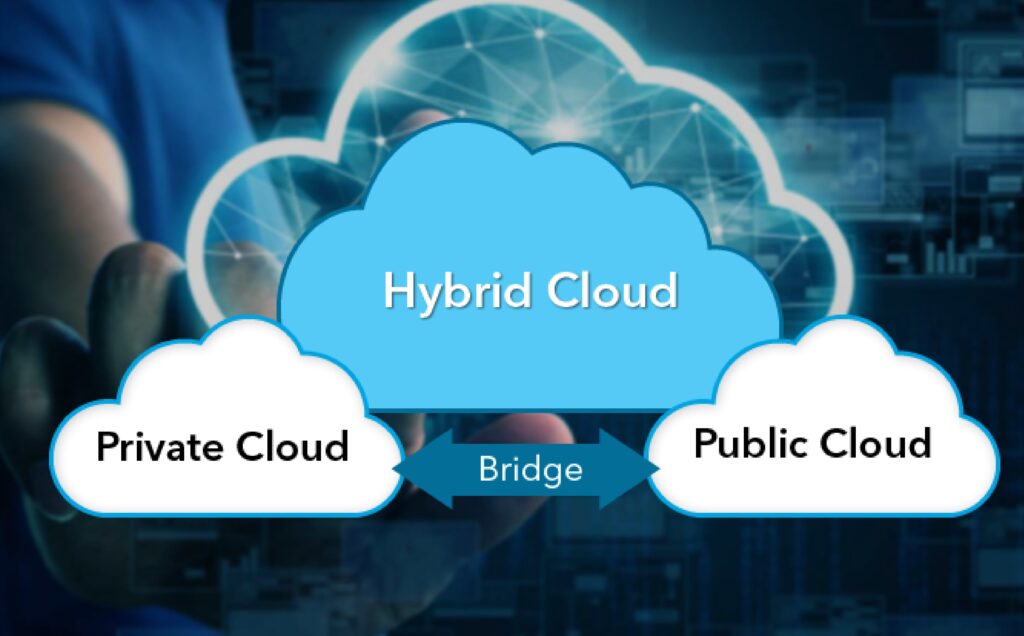
Public Clouds:
These clouds are owned and managed by third-party cloud providers. These provide services on servers and data storage over the internet. Public clouds are accessed by clients through allotted accounts.
Private Clouds:
These are private network services. Their usage is limited to a specific company or organization. Managing the internal data and information of the company through them.
Hybrid clouds:
These clouds are formed by combining Public and private clouds. Hybrid clouds allow flexibility, increased deployment options, and optimization of existing infrastructures.
Types of Cloud Computing:
The three principal types of cloud computing are Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service. Each type of cloud provides different control functions & flexibility.
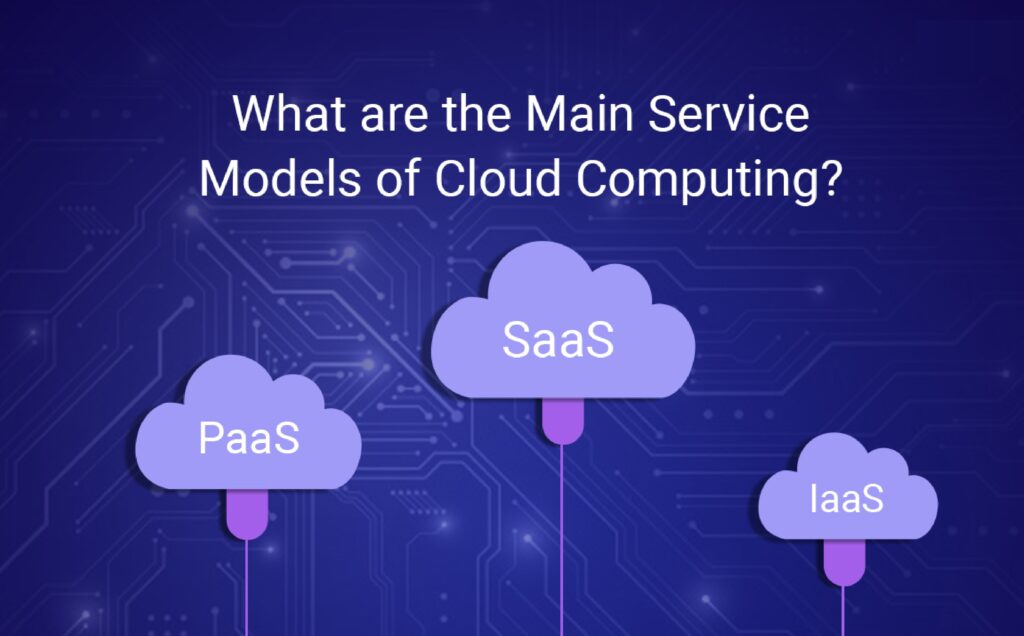
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
IaaS forms the building blocks for cloud services. IaaS is identical to existing conventional IT resources. Hence providing a great degree of flexibility and easily manageable.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
A thorough product that is entirely managed by the cloud provider. With Software as a Service, management and handling infrastructure isn’t the concern of the organization. It’s rather how to utilize the infrastructure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
PaaS removes the need for you to manage underlying infrastructures. Hence allowing you to focus on the practical deployment. Ultimately increasing efficiency.
Edge Computing- The New & Latest Revolution:
Edge computing is based on the concept of bringing computing as nearer to a source of data as possible. In simpler terms, reduced processes within the cloud. Shifting those processes in local places such as in the user’s computer, IoT device, or an edge server. It is necessary to understand the term ‘Edge’. The network edge is where the local network containing the functional device communicates with the internet. The biggest takeaway is that the network edge is geographically close to the device, unlike cloud servers.
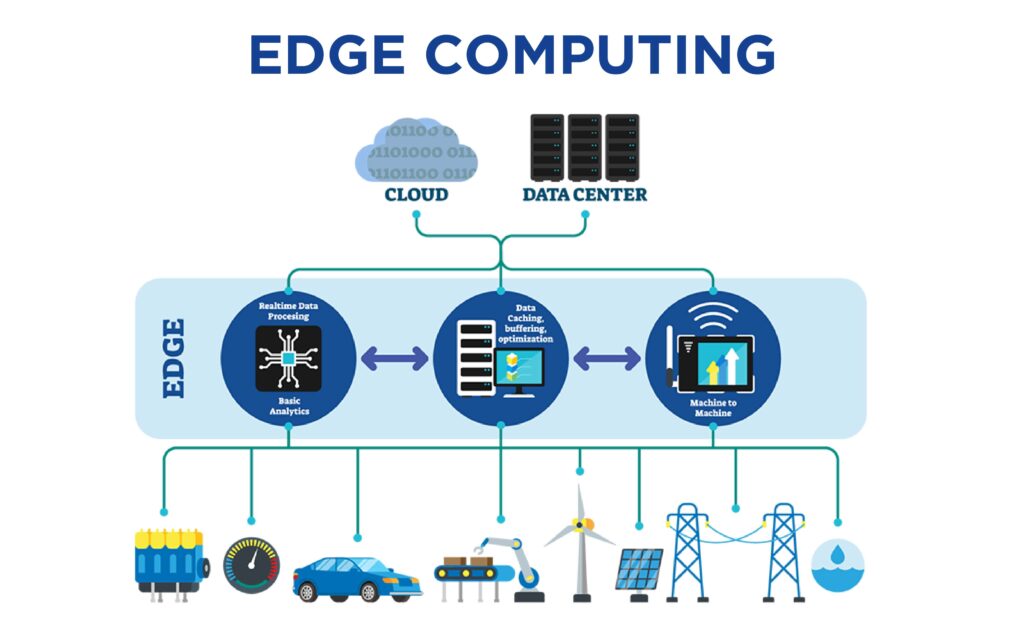
Computing being done at Network’s edge reduces the amount of long distant communication. Maximizing performance, reducing cost & latency are the biggest gains of Edge computing. As we have already seen, using Edge computing reduces the usage of Bandwidth and server resources. With homes & offices getting equipped with printers, thermostats & smart cameras, etc. Managing all these devices requires significant computations to be moved towards the edge.
The biggest benefit of using Edge computing is minimizing latency. With conventional servers, every bit of information is bound to travel large distances before reaching out the desired location. That’s not the case with Edge computing as it makes the perfect usage of existing internal servers to transfer information. Edge computing finds its practical applications in the extensive chain of fields.
It can be used in monitoring assets in the field of oil and gas. Edge computing allows real-time analytics. Alerting the company in case of any breakdown. Healthcare contains various edge computing opportunities. An edge network on the hospital site could process data locally to maintain data privacy. Edge also provides right-time notifications to doctors in case of unusual patient behaviours. Apart from that, it can be utilized in traffic management, cloud gaming & Autonomous vehicles, etc.
Types of Edge Computing:
Depending upon computing resources, Edge computing can be classified into various types.
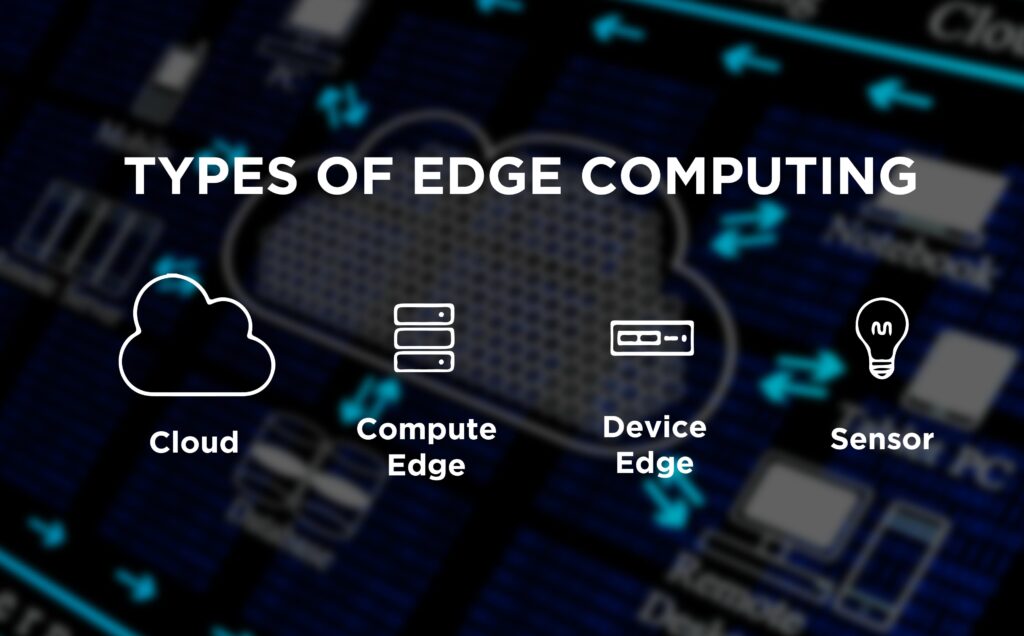
Cloud:
As mentioned, prior, the cloud refers to massive data centres managed by cloud providers.
Compute Edge:
Compute edge is a sort of small data center, containing racks of servers. It is generally placed in the vicinity of IoT devices. The resources in compute edge are not as vast as in the cloud. But is effective in decreasing latency and increased bandwidth.
Device Edge:
Device edge comprises of few small servers and hence has minimal computing capability. But again, the advantage lies in its close location to IoT sensors.
Sensor:
IoT sensors are the controlling devices such as security cameras, bulbs & routers, etc. They don’t have any computing ability. They are dependent on the cloud, compute edge or device edge for computation.
Head-to-Head Comparison:

The idea of cloud computing got popular in 2006 when Amazon launched a product named Elastic Compute cloud. The development and adoption of cloud computing have been tremendous since then. Large organizations have set huge budgets for the very purpose of Cloud computing. On the other hand, the concept of Edge computing emerged in the late 1990s. Similar times to when cloud computing got the early recognition. But the decentralized nature has made the practical adoption taking a longer period. Nonetheless, with its numerous benefits, the huge potential lies within it.
Point of Parity:

Experts believe that both Cloud computing and Edge computing aren’t alternatives to one another. Rather, they see Edge computing as an extension of cloud computing. Instead of indulging in Rivalry. A combination of Cloud computing and Edge computing can take the computing process to a whole new level of excellence. Edge infrastructures with integration to cloud data centres can make up for all the existing loopholes. Although both cloud computing and Edge computing have their distinctions, their combination can provide great value to the end-user experience.
Point of Difference:

The main disparity between cloud computing and Edge computing lies in the way they process the data. Cloud computing with its centralized location, binds information to travel long distances within the designated network. Hence providing a strong control on security protocols. But at the same time, huge distances can cause latency. On the other hand, Edge computing with its decentralized nature. Brings the whole computing process nearer to the source. Decreasing distances and providing real-time data transference. The operating nature of edge computing exposes it to potential security threats.
Looking at the Future:

Cloud computing has been a blessing in disguise for organizations looking for increased capacity at minimal expenditures. But the infrastructure with its latency issues possesses problems to the future of cloud computing. While Edge computing has infinite future potential stored within it. The capabilities of edge architecture to increase the speed of data processing, minimizing time lag ensures sustainable development and growth in autonomous fields is what makes it is future bright.
Bibliography and references:
[1] https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/cloud-computing.asp
[2] https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/serverless/glossary/what-is-edge-computing/



